- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录3878 > PIC18F4610T-I/ML (Microchip Technology)IC MCU FLASH 32KX16 44QFN
PIC16F87XA
DS39582B-page 182
2003 Microchip Technology Inc.
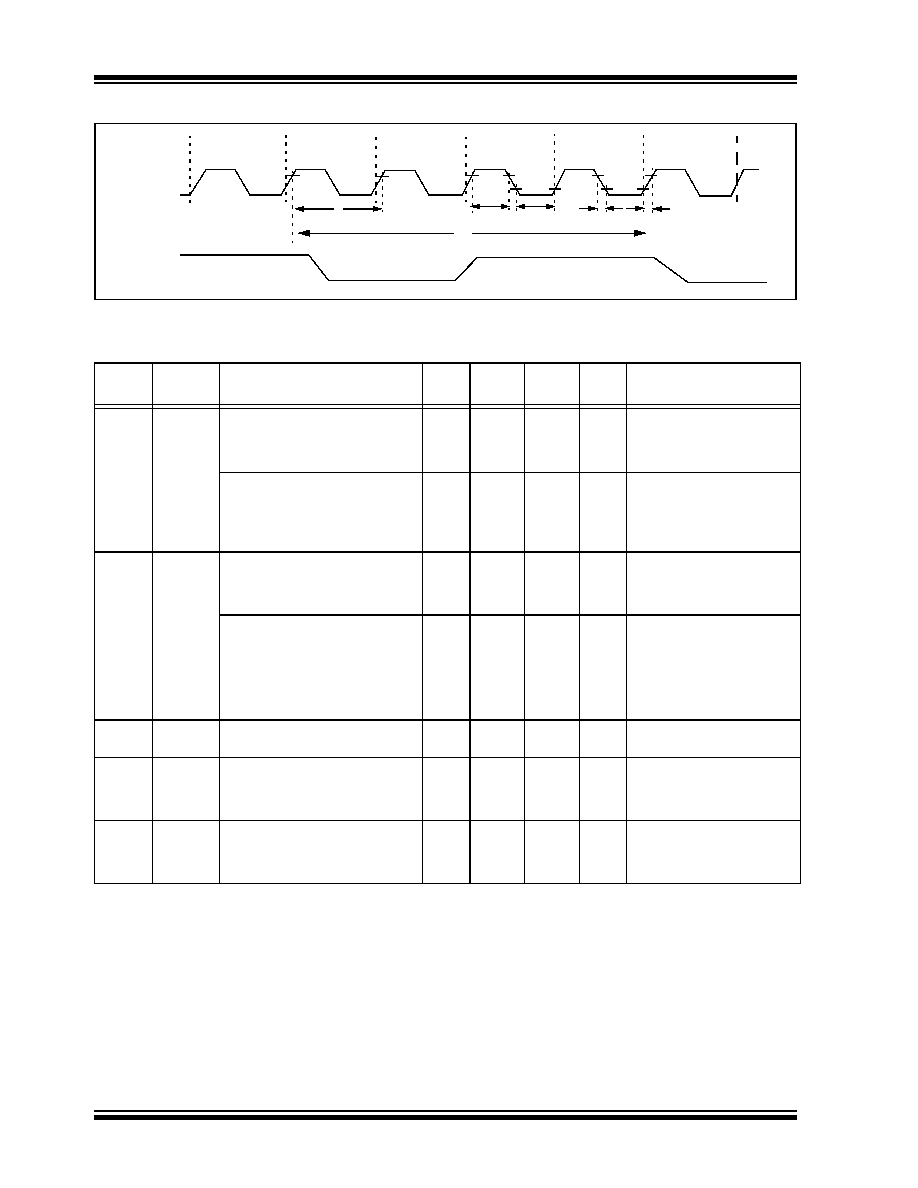
FIGURE 17-4:
EXTERNAL CLOCK TIMING
OSC1
CLKO
Q4
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q1
1
2
3
4
TABLE 17-3:
EXTERNAL CLOCK TIMING REQUIREMENTS
Param
No.
Symbol
Characteristic
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
FOSC
External CLKI Frequency
(Note 1)
DC
—
1
MHz
XT and RC Osc mode
DC
—
20
MHz
HS Osc mode
DC
—
32
kHz
LP Osc mode
Oscillator Frequency
(Note 1)
DC
—
4
MHz
RC Osc mode
0.1
—
4
MHz
XT Osc mode
4
5
—
20
200
MHz
kHz
HS Osc mode
LP Osc mode
1TOSC
External CLKI Period
(Note 1)
1000
—
ns
XT and RC Osc mode
50
—
ns
HS Osc mode
5—
—
sLP Osc mode
Oscillator Period
(Note 1)
250
—
ns
RC Osc mode
250
—
1
s
XT Osc mode
100
—
250
ns
HS Osc mode
50
—
250
ns
HS Osc mode
31.25
—
sLP Osc mode
2TCY
Instruction Cycle Time
(Note 1)
200
TCY
DC
ns
TCY = 4/FOSC
3TOSL,
TOSH
External Clock in (OSC1) High or
Low Time
100
—
ns
XT oscillator
2.5
—
s
LP oscillator
15
—
ns
HS oscillator
4TOSR,
TOSF
External Clock in (OSC1) Rise or
Fall Time
—
25
ns
XT oscillator
—
50
ns
LP oscillator
—
15
ns
HS oscillator
Data in “Typ” column is at 5V, 25°C unless otherwise stated. These parameters are for design guidance
only and are not tested.
Note 1:
Instruction cycle period (TCY) equals four times the input oscillator time base period. All specified values are
based on characterization data for that particular oscillator type, under standard operating conditions, with
the device executing code. Exceeding these specified limits may result in an unstable oscillator operation
and/or higher than expected current consumption. All devices are tested to operate at “min.” values with an
external clock applied to the OSC1/CLKI pin. When an external clock input is used, the “max.” cycle time
limit is “DC” (no clock) for all devices.
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
PIC18F4610-E/PT
IC MCU FLASH 32KX16 44TQFP
PIC18F4610-E/ML
IC MCU FLASH 32KX16 44QFN
PIC18LF2331T-I/SO
IC MCU FLASH 4KX16 28SOIC
PIC18F4515T-I/PT
IC MCU FLASH 24KX16 44TQFP
PIC18F4431T-I/ML
IC MCU FLASH 8KX16 44QFN
PIC18F4431-E/ML
IC MCU FLASH 8KX16 44QFN
PIC18F4410T-I/ML
IC MCU FLASH 8KX16 44QFN
PIC18F4410-E/PT
IC MCU FLASH 8KX16 44TQFP
相关代理商/技术参数
PIC18F4610T-I/PT
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 64KB 3968 RAM 36 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4620-E/ML
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 64KB 3968 RAM 36 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4620-E/P
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 64KB 3968 RAM 36 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4620-E/PT
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 64KB 3968 RAM 36 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4620-E/PT
制造商:Microchip Technology Inc 功能描述:IC 8BIT MCU PIC18F 40MHZ TQFP-44 制造商:Microchip Technology Inc 功能描述:IC, 8BIT MCU, PIC18F, 40MHZ, TQFP-44
PIC18F4620-I/ML
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 64KB 3968 RAM 36 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4620-I/P
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 64KB 3968 RAM 36 I/O RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4620-I/P
制造商:Microchip Technology Inc 功能描述:IC 8BIT FLASH MCU 18F4620 DIP40